HFM-RP4: Magnetoplethysmograph for Continuous Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Monitoring
Principal Investigator: Professor Wu Yihong, ECE
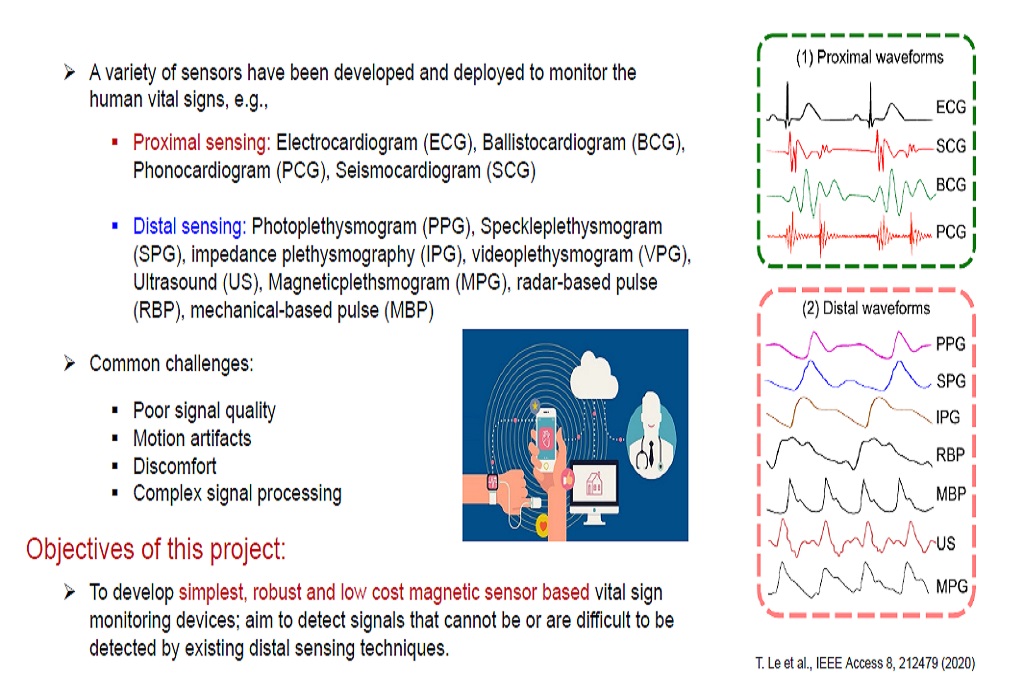
Wearable health monitoring devices with high accuracy and ease of use and comfort are highly demanded for continuous monitoring of an individual’s health condition. Currently almost all wearables use a method called photoplethysmography (PPG) to measure the volumetric variations of blood circulation, from which heart rate (HR), breathing rate (BR), blood pressure (BP), and many other biometrics can be extracted. However, most products currently on the market suffer from motion artifacts during daily activities such as physical exercise, housework, office work, etc. Since light has to pass through the skin, it is also affected by the tone of skin. Although various alternative techniqueshave been proposed, each of these methods has its own strength and limitations. The objectives of this project are to
(i) demonstrate the technical feasibility of a magnetic based wearable heart rate and blood flow monitoring device that is less sensitive to motion artifacts and change of tone of skin,
(ii) develop algorithm to improve the accuracy of measurement results through benchmarking with other techniques, and (iii) demonstrate the ability to collect real-time data from human objects in different age groups.