-
- ARIS-RP1: Design and Characterization of Ultra-Large-Scale Intelligent Electromagnetic Surfaces Using Deep Learning
- ARIS-RP2: Reprogrammable Meta-optics for Information Multiplexing
- ARIS-RP3: Making Wireless Communication Environment Smart via Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS): A New Network Optimization Perspective
-
- FCT-RP1: Practical Data Storage and Computation in DNA Molecules
- FCT-RP2: Amorphous-Oxide-Semiconductor Thin Film Transistors and DRAM Cross-bar to Enable 3D Monolithically Integrated Architecture for Near/In-memory Computing
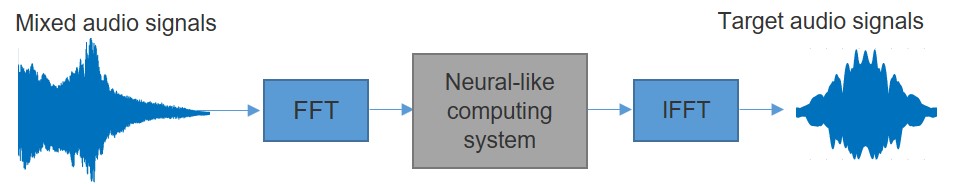
- FCT-RP3: Neural-like Computing System based on Superparamagnetic Tunnel Junctions
-
- HFM-RP1: Wearable Microneedle Patch for the Minimally Invasive Wireless Continuous Glucose Monitoring
- HFM-RP2: On-body computing for Next-generation Wearable Systems
- HFM-RP3: A Novel Optical Biometer to Monitor Myopia Progression in Children.
- HFM-RP4: Magnetoplethysmograph for Continuous Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Monitoring
- HFM-RP5: Manufacturing of Artificial SKin Integrated Network (SKIN) for Healthcare and Fitness Monitoring
- HFM-RP6: Radio-frequency Textile Sensors for Wearable and Ambient Health Monitoring
-
- ADT-RP1: Development of High Precision Additive Manufacturing for Integrated Complex Molding Applications
- ADT-RP2: Low Loss and Tunable Ferroelectrics for Sub-6G Applications
- ADT-RP3: Redox-mediated Flow Battery for Household Energy Storage
- ADT-RP4: Development of Nature-inspired Multiscale Composite Materials for High Strength and Low Loss Applications
-
- WDSS-RP1: Enabling Continuous and Realtime Monitoring of Human Vitals through Battery-free Tunnel Diode based Sensors
- WDSS-RP2: Wireless Communication and Radar Sensing Fusion Based Indoor Localization
- WDSS-RP3: Multi-parameter Sensing Platform for Proactive Hypertension Diagnostics Using Artificial Intelligence
- WDSS-RP4: LightChips: Light-Based Integrated Cloud-to-Edge Communications, Sensor Node Wake-Up and Indoor Positioning for mm-Scale Purely-Harvested Systems
FCT-RP3: Neural-like Computing System based on Superparamagnetic Tunnel Junctions
Principal Investigator: Professor Yang Hyunsoo, ECE
Recently, significant research efforts have been made to find alternative computing architectures than traditional von Neumann one, where the transfer of data between physically separate logic and memory blocks results in processing bottlenecks and significant power consumption. We aim to demonstrate a real-time neural-like computing system implemented using ultra-low power stochastic magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJ). It is a novel computing system which uses neural-like devices for computing and non-volatile magnetic devices for storing. This architecture provides substantially low power consumption and fast calculation by physically emulating neurons at the very low device and circuit level.
As a final demonstration, we will apply such a computing system in mimicking a brain’s function, in particular, for an audio signal separation task. Audio signal separation has been one of the most difficult tasks in the audio signal processing area with a great potential in speech recognition, simultaneous interpretation, chatting robots, security monitoring, self-driving car and so on. Although advances in audio signal separation have led to a performance improvement in challenging scenarios such as noisy and far-field conditions using various artificial neural networks (ANNs), it still performs poorly when the signal source of interest is recorded in crowded environments and when the number of signal sources increases. We aim to do a real-time separation of the audio signals of a target source from multi-source signals with a low latency, power consumption, and error rate.