Bimanual Grasping Robot with 6 DoF Arms
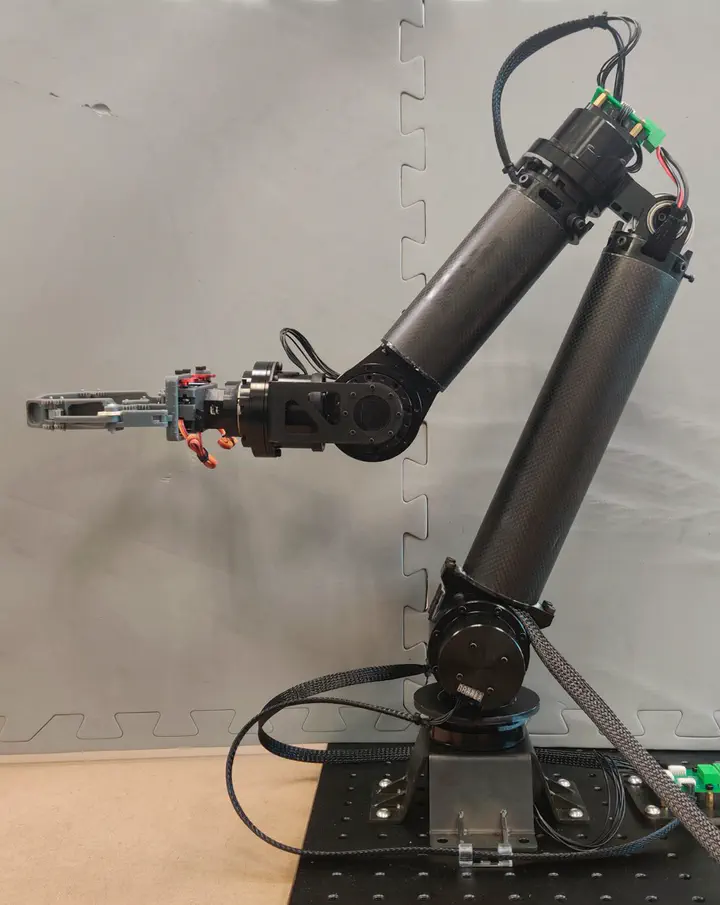

Bimanual grasping is an important research area in the field of robotics and automation. It involves the use of two robotic arms to work cooperatively in a human-like manner to complete the task of grasping and manipulating objects. This collaborative operation can improve efficiency and precision, allowing robots to handle complex tasks such as assembly, handling, and maintenance, and be used in fields such as industrial automation, medical surgery, warehousing and logistics, military, and space exploration. However, realizing bimanual grasping involves many challenges, including object detection and recognition, grasping point planning, collaborative control, path planning, etc. Researchers need to overcome these difficulties to achieve an efficient and reliable grasping task with two robotic manipulators.
Hence, a 6 degree-of-freedom (DoF) manipulator that contains joint torque control mode and full dynamic model is proposed. It is 3.5kg weight per arm with maximum 1kg payload at 0.6 m full extension. The manipulator is made of carbon fiber, aluminum alloy and other lightweight materials. To further reduce the dynamic effect, the elbow joint is driven by an actuator mounted at the shoulder via a timing belt transmission.
Finite State Machine (FSM) is implemented to the manipulator in order to manage all states of the manipulator in case of any unexpected states.
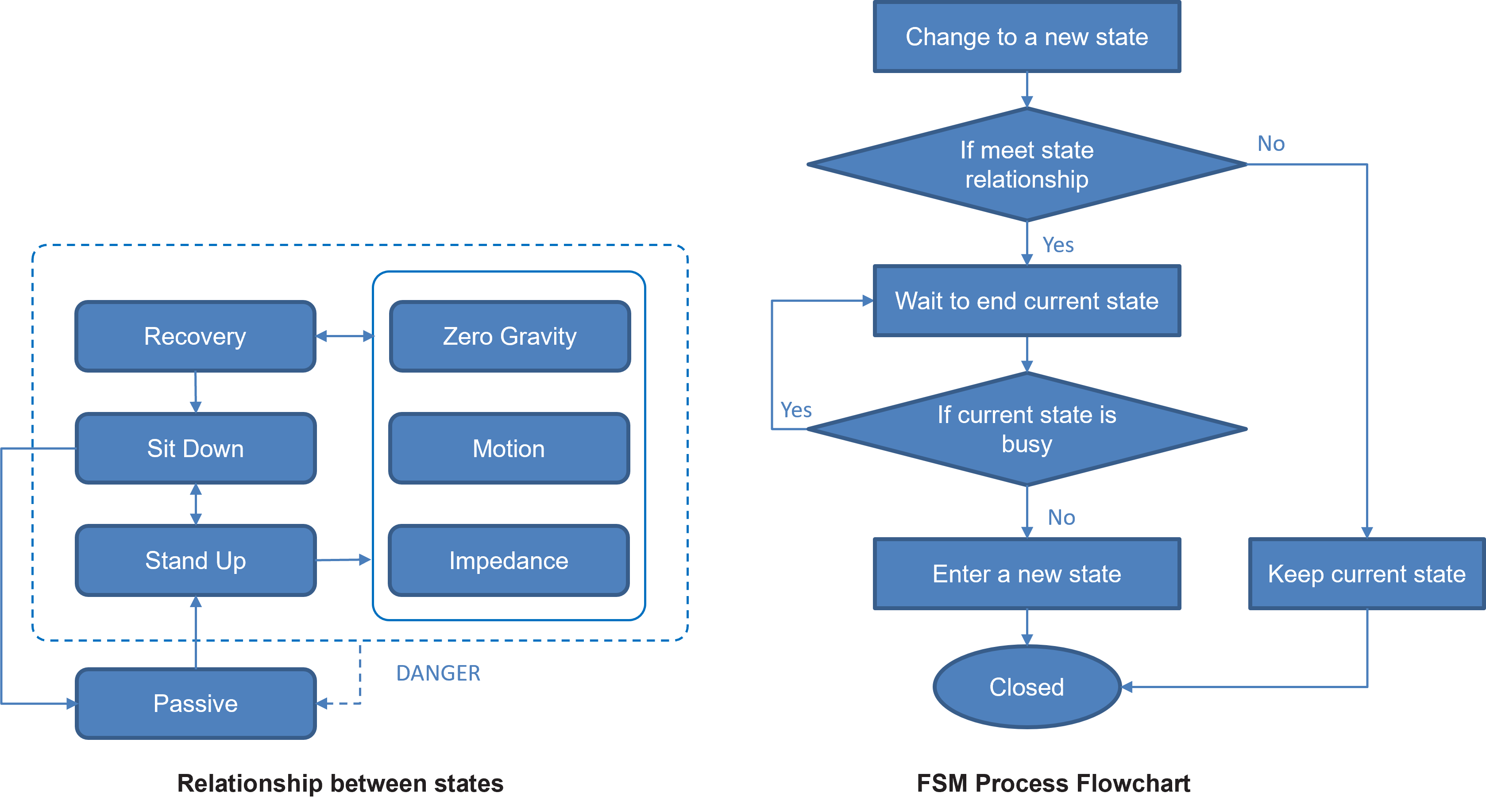
Finite State Machine
Experiment results and performance reflected that the NUS manipulator has a better track performance and a more accurate dynamic model.
Moreover, it can be installed on a bimanual robot, acting as its arms, which also shows good and accurate track trajectories.

