Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) Actuators and Mechanisms
Design Test Device
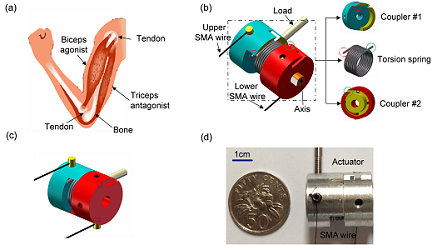
SHAPE Memory Alloy (SMA), as an artificial muscle, can remember its original shape at a low temperature and return to the pre-deformed shape by heating. SMA actuators possess the advantage of mechanical simplicity, high power to weight ratio, small size and noiseless operation. We focus on the design, modelling, and control of novel compliant differential (CD) SMA actuators and mechanism to achieve higher range of motion and faster response. These actuators can have wide applications in medical robotics and bio-inspired Robotics. This CD SMA actuator, composed of two antagonistic SMA wires and a mechanical joint coupled with a torsion spring, has significantly improved performance compared to traditional SMA actuators. The differential SMA wires are utilized to increase the response speed, and the torsion spring is employed to reduce the total stiffness of SMA actuator and improve the range of motion. The variable structure control (VSC) strategy, which is robust in nonlinear system with parameter uncertainties, is applied to enhance control performance for the compliant actuator. Experimental results prove that this new actuator can provide larger output range of motion compared to conventional SMA actuators under the same conditions.

