Air Pollution
Traffic Pollutant Dispersion (Urban Scale)
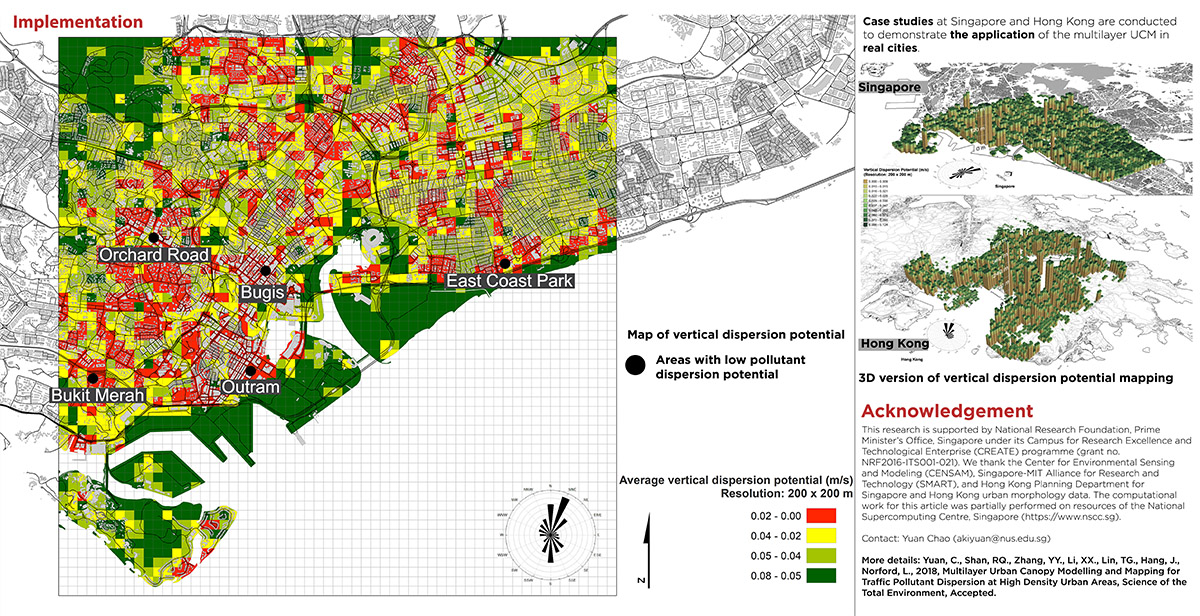
GIS Tool_Modelling and Mapping for Traffic Pollutant Dispersion at Urban Areas
Numerical simulation and Wind tunnel are too expensive to be used simulating pollutant dispersion at street canyons for urban planning and design practice.
This study aims to develop a new semi-empirical model to evaluate the effect of heterogeneous urban morphology on traffic air pollutant dispersion, which has the direct impact on public health. A multilayer urban canopy model (MUCM) is developed to include the impact of building height variance on pollutant dispersion, and we validate the new model by cross-comparing the results from Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation.
Furthermore, two case studies are conducted to illustrate how to implement MUCM in the planning practice in metropolitan areas in Singapore and Hong Kong. With an in-house GIS team using available data, MUCM provides urban planners a way to understand traffic air pollutant dispersion in high-density urban areas.
Outputs:
- We create a practical model to estimate vertical pollutant dispersion potential;
- The model is derived based on understandings of mass and momentum conservation;
- Friction velocity, representing momentum flux, is modelled and validated;
- We clarify the effect of heterogeneous urban spatial characteristics on air pollutant dispersion.
Publication:
- Yuan C, Shan RQ, et al., 2019, Multilayer Urban Canopy Modelling and Mapping for Traffic Pollutant Dispersion at High Density Urban Areas, Science of the Total Environment, 647, pp 255-267.
Conference Presentation:
- Yuan C, Shan R, Zhang Y, Li XX, Yin T, Norford L, 2019, Semi-empirical modelling and mapping of traffic pollutant dispersion at high density urban areas for livable and resilience cities, Proceeding in European Meteorological Society (EMS), Copenhagen, Denmark.
- Yuan C, Shan RQ, Zhang YY, Li XX, Yin T., Norford LK, 2018. Multilayer Urban Canopy Modelling and Mapping for Traffic Pollutant Dispersion at High Density Urban Areas, Proceeding In Passive Low Energy Architecture Design to Thrive (PLEA). Hong Kong, China.
- Yuan C, Shan RQ, Li XX, Yin T., Norford LK, 2018. Multi-layer Urban Canopy Model for Traffic Pollutant Dispersion at High Density Urban Areas. Proceeding in the 10th International Conference on Urban Climate (ICUC 10). New York, U.S.

Figure. Traffic at downtown, Singapore.