Natural Ventilation
Vertical Farming (Building Scale)
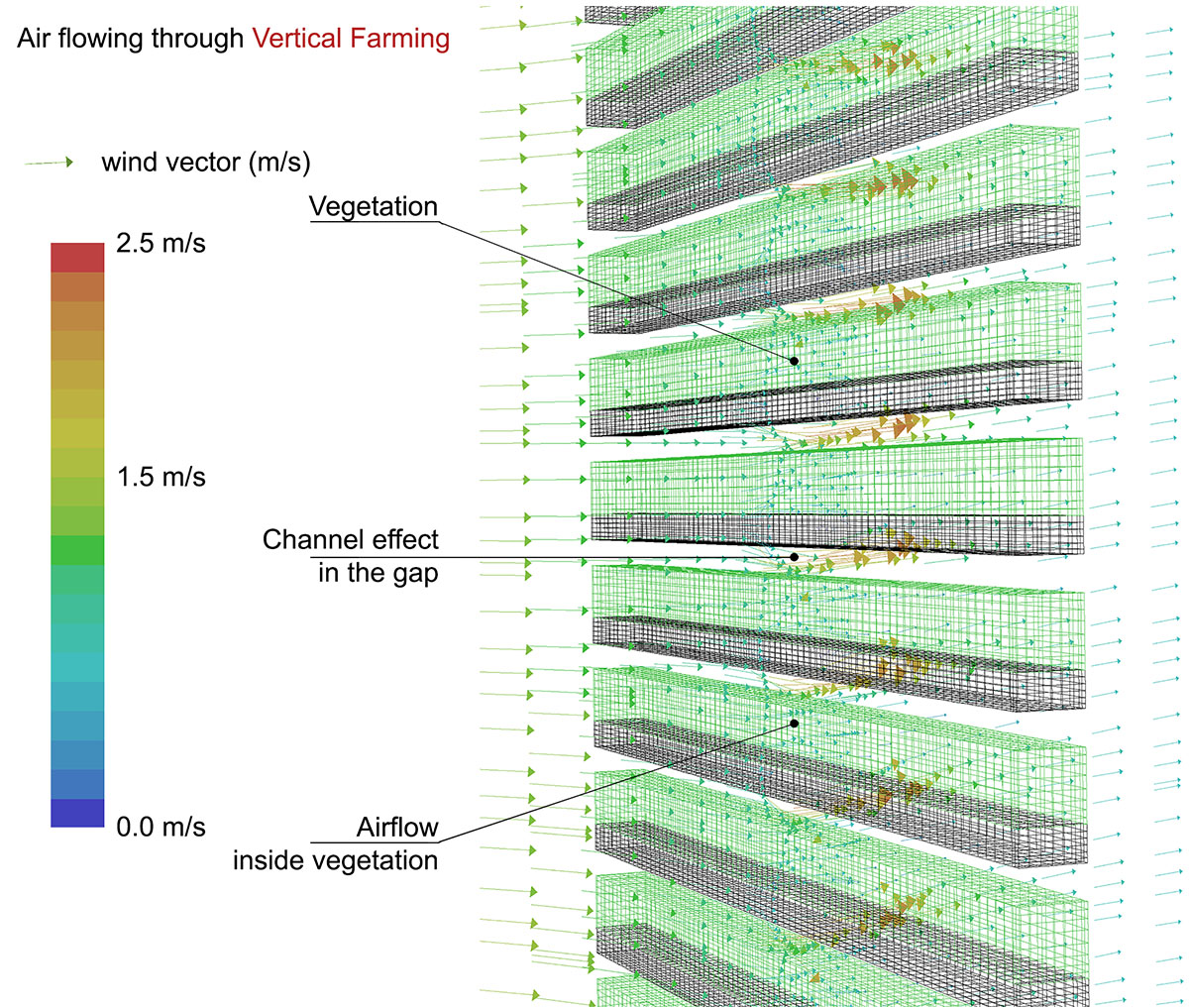
While vertical farming can promote sustainable living and mitigate urban heat island, it could worsen the cross natural ventilation due to additional drag force on air flow.
This study aims to investigate the impact of vertical farming on ventilation performance that is important to thermal comfort, especially in tropical/subtropical cities. The Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation was first validated against the wind tunnel experiment in the street canyon with tree planting. The vegetable was modelled as a porous medium in CFD simulation. In the parametric study, six configurations of facades module were investigated with respect to the vegetable block ratio, arrangement, and vegetable species.
This study provides important understandings on vertical farming to enable architects to make evidence-based decision in architectural design.
- The CFD simulation was validated against the wind tunnel experiment in the street canyon with tree planting;
- A validated Reynolds Stress Model (RSM) turbulence model was used to successfully simulate the dynamics of air flow and emission dispersion with tree planting as a porous medium in the street canyon;
- The results of the parametric study indicate that the natural ventilation performance is highly affected by the block ratio of vegetable;
- The natural ventilation with the same block ratio of vegetable could be improved by appropriately modifying the vegetable arrangement and vegetable species;
- The above understandings provided by this study enable architects to make scientific evidence-based decisions during building envelope design with vertical farming.
Publication:
- Yuan C*, Shan RQ, Adelia AS, Tablada A, Lau SK, Lau SSY, 2019, Effects of Vertical Farming on Building Cross Natural Ventilation at Urban Residential Areas, Energy and Buildings, 185, pp 316- 325.
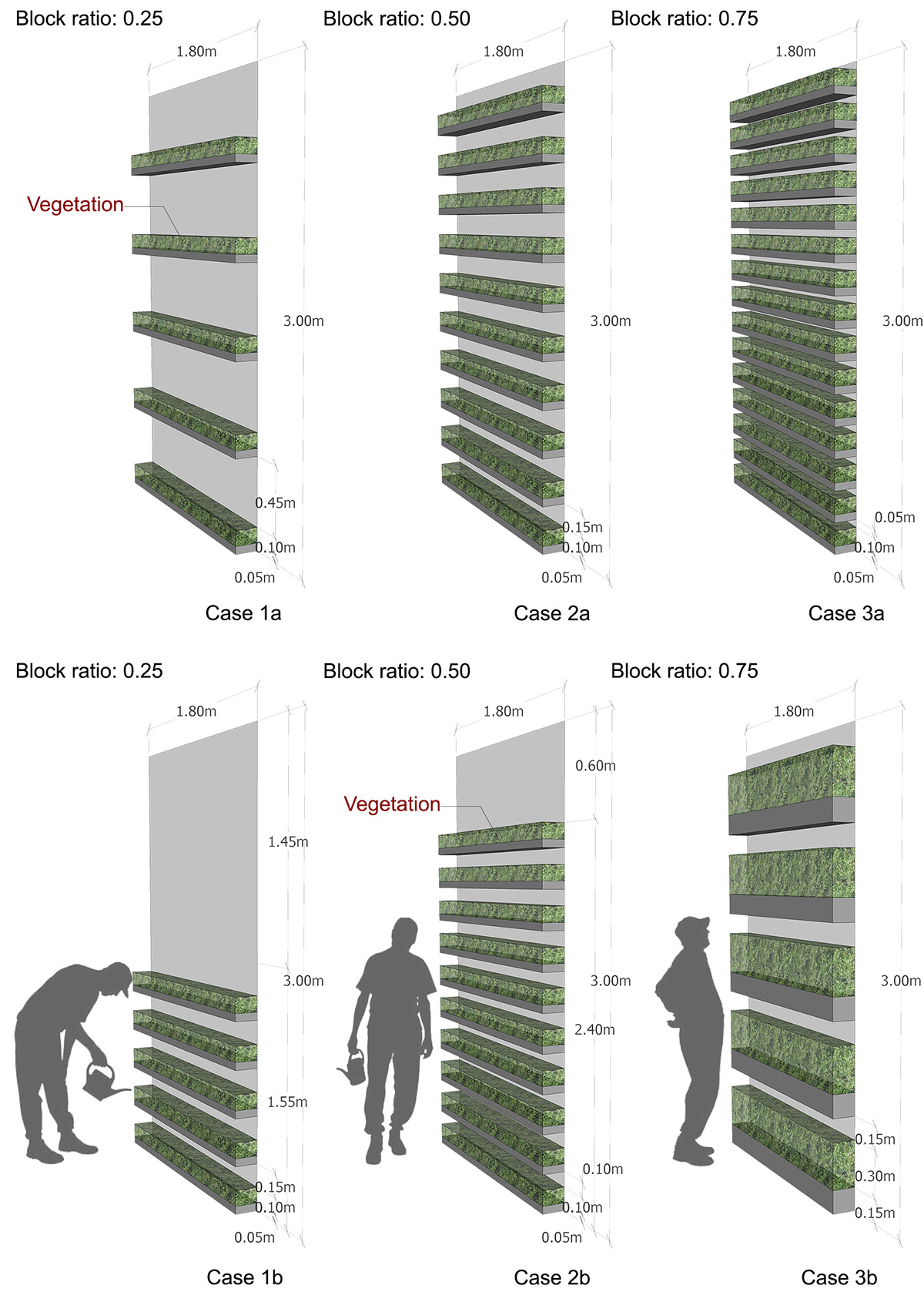
Figure. Layouts of vertical farming.
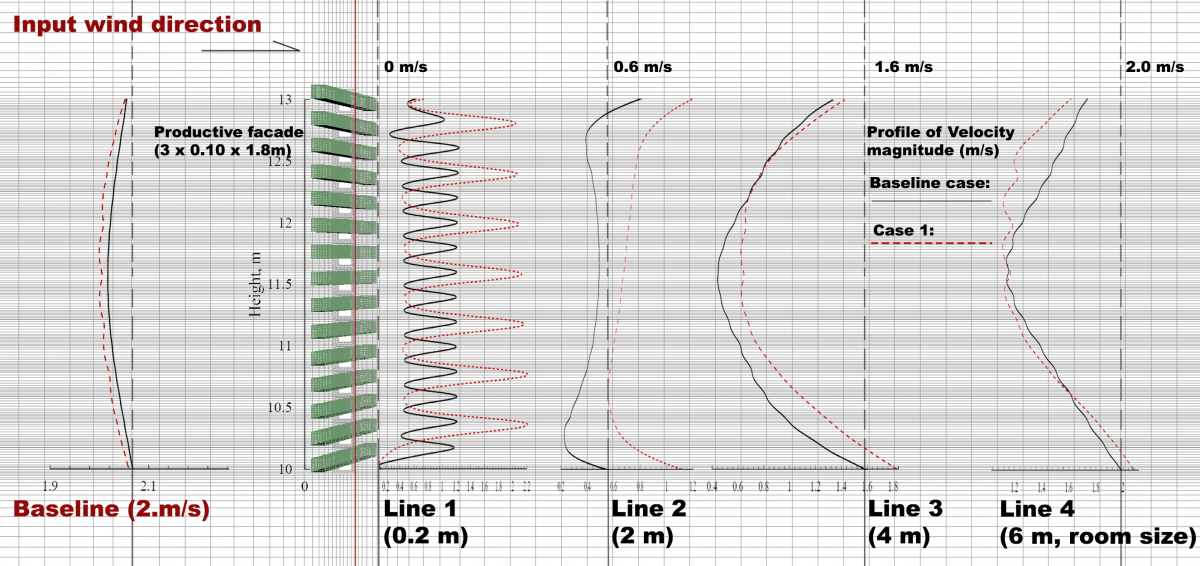
Figure. Quantitative analysis on cross natural ventilation.