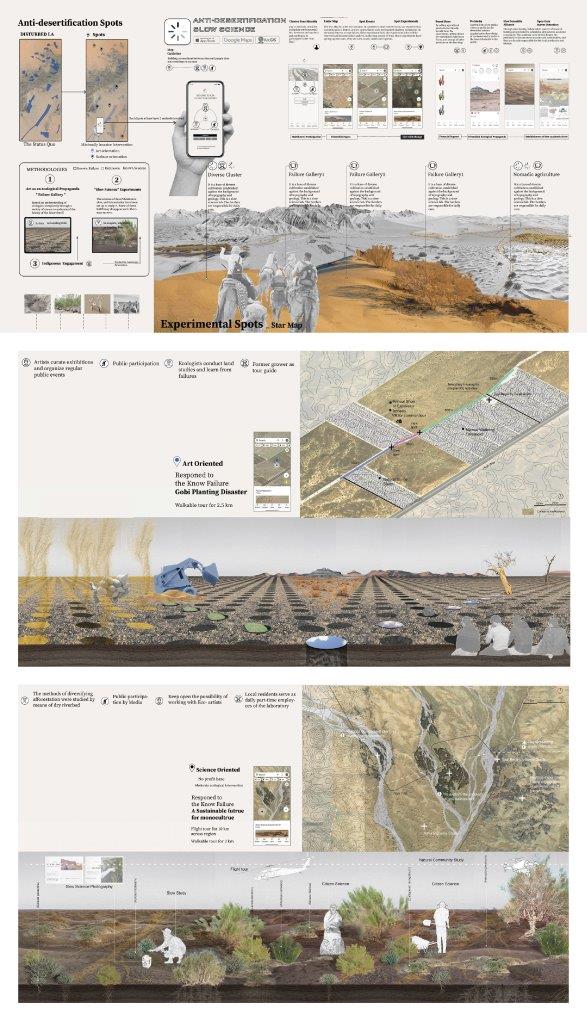
Atlas & Land art & Slow Science Experiments to open up the political imaginary
PROGRAMME
Master of Landscape Architecture
STUDENT
Wang Junyu
YEAR
2
ADVISOR/TUTOR
Maxime Cedric Decaudin
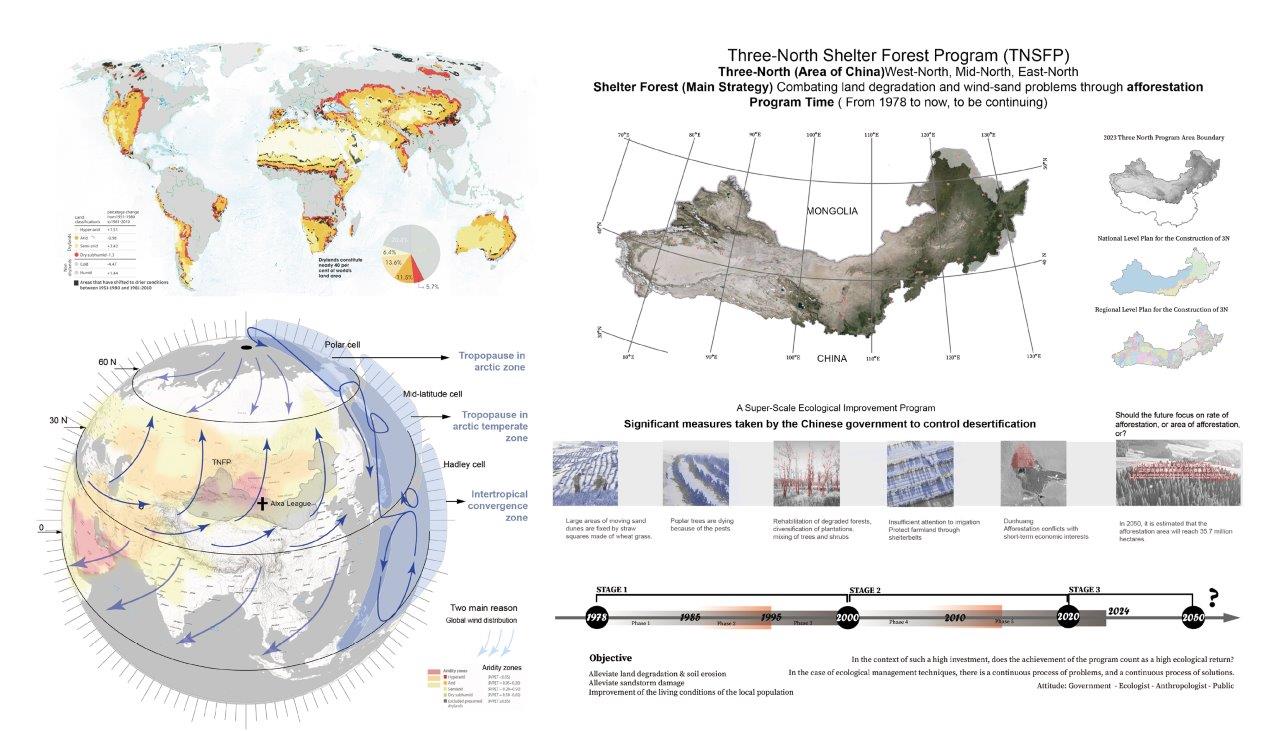
As a result of dust storms and land degradation caused by Desertification, the Chinese government implemented the Three-North Shelter Forest Program (TNSFP) in 1978, and the land was reshaped by top-down planting activities in the course of this huge ecological project. Through historical analysis, and analysis of typical events, some conclusion and position came up. In the face of large-scale ecological policies, one-to-one causal relationship is not applicable. There are problems that cannot be solved or explained by existing policy frameworks and scientific understanding. We should be aware of the limits of existing political imaginary.
Alxa, a region in Inner Mongolia province, has a fragile ecological environment. Its geographical conditions are also complex, with three sandy deserts. Ecological vulnerability and location characteristics has led to a strict grazing ban and afforestation policy. With many years of practice developed, represented by Haloxylon ammodendron (Suosuo) and Cistanche deserticola (Roucongrong), there are sand-fixing plantation and cash crops on this barren land. Although the TNSFP has helped some herders restore their livelihoods, inappropriate afforestation and cultivation has exacerbated the vulnerability of the unique ecosystems in the Alxa region.
This design thesis hopes to use one non-spatial means: atlas; one online method: desert edge; two methods of space: land art and slow science experiments. The object is to express the complexity of ecological understanding, open up the political imaginary and promote the effective process of combating desertification by increasing the participation of indigenous people. Atlas is a problem showing position, showing the unknown and chaos in desertification process. The design spots, as a problem solving position, do slow science experiments with small venues, celebrate past failures with land art as a diverse ecology advocacy, and embrace any possible future results.
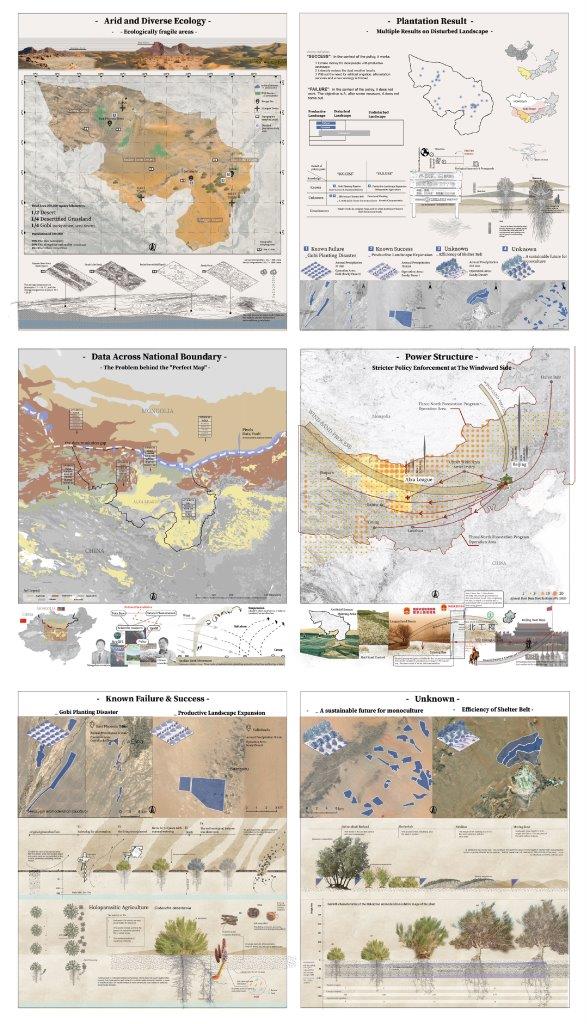
Data Across National Boundaries
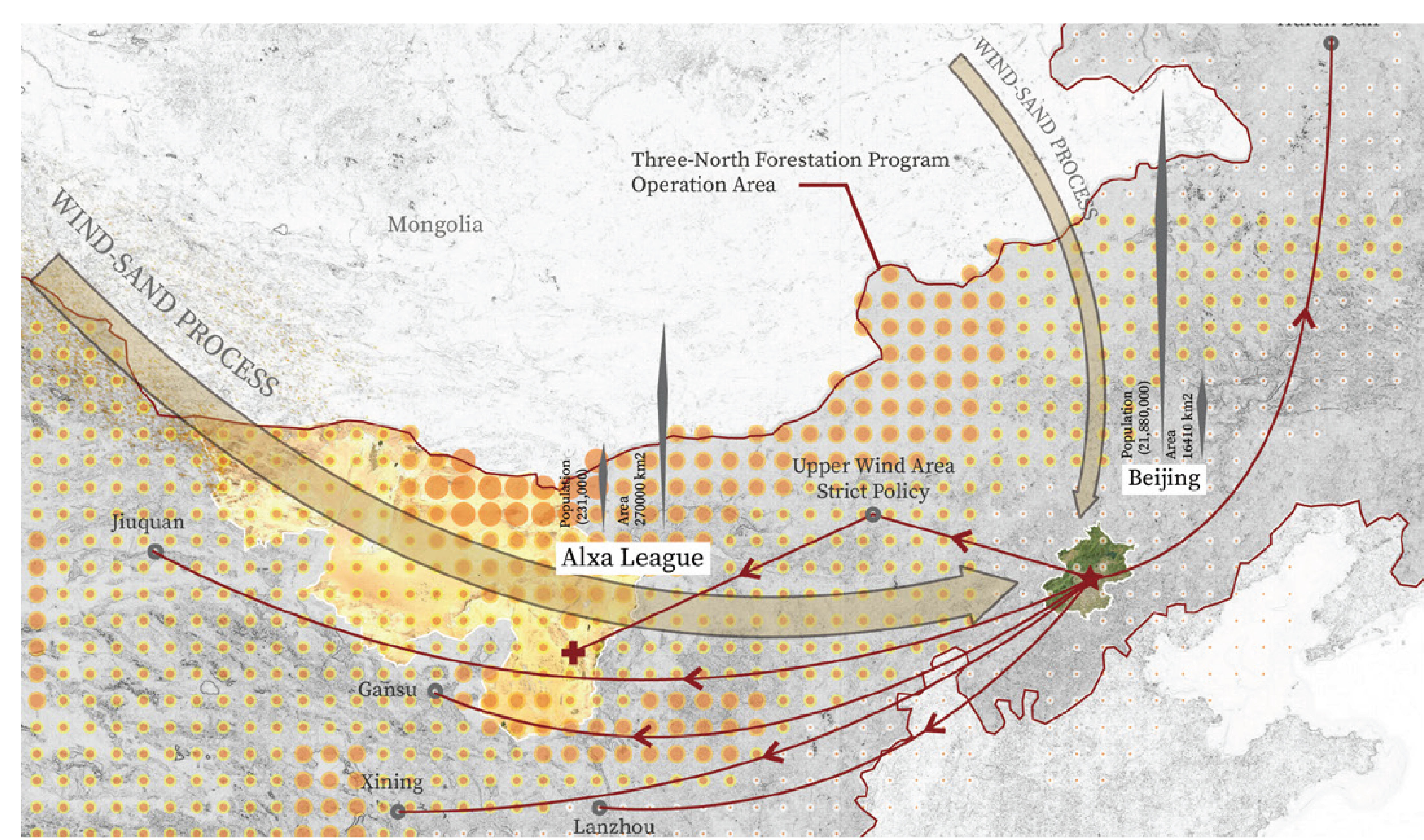
As the open source data in arcgis, there are some data segment faults and loss. The Mongolia and China part has a data resolution gap. The data across the national boundary mattered. Because when the scientists study the aeolian Sand Movement, the accurate soil condition is crucial. The Sand doesn’t stop at the boundary, they keep going on but the the data stop at the boundary. Such problems are difficult to solve because of policy or academic and data transnational communication.
Power Structure
The Alxa is upwind of Beijing. The dusty weather in Beijing is partly attributed to it. So the ecological Bans is quite strict in Alxa. The herders there are banned to grazing. They got financial support from Beijing to do plantation. In large ecological policies, such power structures are unavoidable. The Alxa and Beijing are responsible for each other.
Diverse Ecology
Alxa is a district in the Inner Mongolia of China at the edge of the Gobi desert. One half of the land here is desert, one quarter is Gobi, rocky or semi desert, and one quarter is desertified grassland. The ecology here is fragile and the geology is diverse.
It can be seen that the outcomes under the policy framework have success and failure, and the natural understanding is so diverse. In these disturbed landscape lands, known successes, known failures, and unknown futures. I’ll take a quick look. These will help me design my spots.
Known and Unknown
Beacause of a severe lack of rainfall in the area, suosuo was kept alive for three years by artificial watering. There is a surface like a shell on Gobi, and when the hole is dug, the sand inside is released, causing damage to the land. The extensive productive land expansion of Deserticola (parasitic rare desert herb) can affect soil microbial flora.
The shelterbelts on the northern side of Jertai salt lake have been in place for almost 40 years. It is used to prevent dust. But it is not until 2023 that relevant papers have used scientific methods to monitor the data of wind-blown sand to quantify its exact effect. So we expect a more precise future.
For artificial suosuo forests that have been successfully planted, the scientists examined populations of different ages and found that the monoculture population over 9 years old had relatively significant salinization.
Beacause of a severe lack of rainfall in the area, suosuo was kept alive for three years by artificial watering. There is a surface like a shell on Gobi, and when the hole is dug, the sand inside is released, causing damage to the land. The extensive productive land expansion of Deserticola (parasitic rare desert herb) can affect soil microbial flora.
The shelterbelts on the northern side of Jertai salt lake have been in place for almost 40 years. It is used to prevent dust. But it is not until 2023 that relevant papers have used scientific methods to monitor the data of wind-blown sand to quantify its exact effect. So we expect a more precise future. For artificial suosuo forests that have been successfully planted, the scientists examined populations of different ages and found that the monoculture population over 9 years old had relatively significant salinization.
The failure gallery tour response to the Gobi planting Disaster. The hollows left by the dead suosuo become an holes array, and people will slowly walk through this artificial sublime. There will be a 2.5km walkable tour.
The concave is the scare of land. Most of them are backfilled, some are left behind, and a smaller part forms straight lines in the matrix. Mirror, Grass mat, black paint holes, cross-over. The vividness of the excavator is an external object,an Instrument of land invasion. And the tornado in vr is an extreme imagination of the wind-blown sand slowly released from the concave.
The dry riverbed diverse biome study responed the unknown futrue of monocultrure . Three clusters were placed on the dry riverbed to study artificial afforestation simulating nature. The slow process of desert vegetation ecosystem was summarized through experiments. Outsiders can fly over this slow-growing area by the route of a plane.
This is not a phalanx of trees, but a place of experimentation for understanding and imitating the massy natural groups of desert plants, which we accept as unordered, as savage growth.