Assoc Prof Rudi Stouffs and his Team Awarded buildingSMART International Special Distinction in Innovation
AUTHOR
Rudi Stouffs, Principal Investigator
Prof Rudi Stouffs and his team received the “buildingSMART International Special Distinction in Innovation” at the buildingSmart International Standards Summit 2019 in Beijing for the research done in the “Strict and automatic mapping of IFC-BIM models into semantically enriched 3D CityGML building models (exterior and interior)” project for GovTech and NRF.
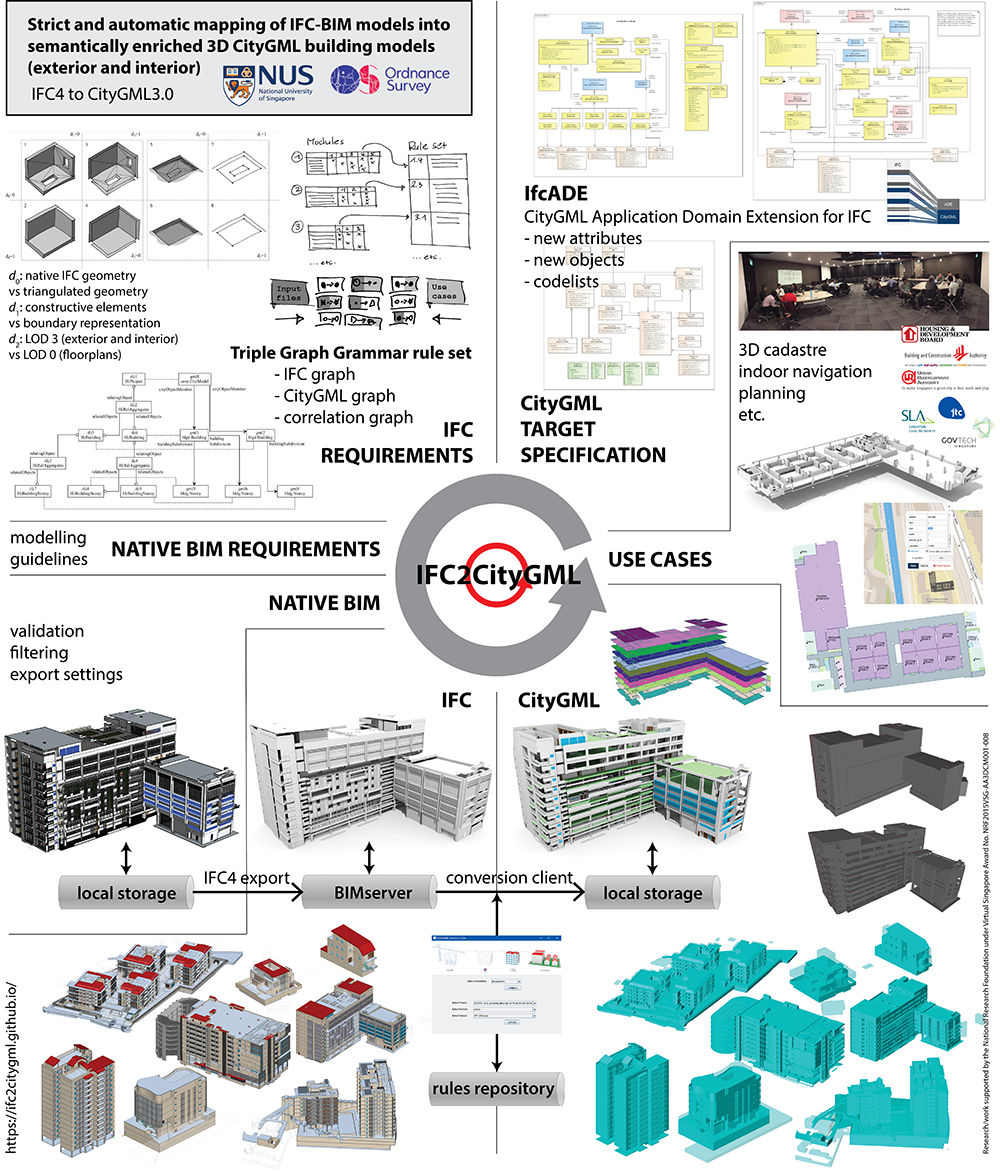
With the aim to develop a methodology and algorithms to automate the mapping and conversion of Building Information Modelling (BIM) models in the IFC format into geospatial building models in the CityGML format (as has been adopted by Virtual Singapore), the IFC2CityGML project (a collaboration between NUS and Ordnance Survey) resulted in a minimum viable product that successfully converts real world BIM models into CityGML models. The resulting conversion addresses not only exterior building elements but also interior structures, including corridors, rooms, internal doors and stairs.
At the same time, it includes semantic information as well as geometry that can be extracted from the BIM model, such as information about spaces, accessibility, materials, etc. Such semantic information is important for analysis and simulation, such as wayfinding, egress, energy use, daylighting, air flow, etc. In collaboration with various government agencies, including Govtech, HDB, BCA, SLA, URA and JTC, we explored a large range of potential use cases, in order to understand the requirements for a complete and near-lossless mapping. In order to allow the embedding of all this semantic information in a useful way within the CityGML format, we developed an Application Domain Extension for CityGML, effectively supporting the incorporation of semantic information from the BIM models into CityGML building models.
For mapping and conversion we adopted a rule-based methodology to map the graph representations of IFC and CityGML are manifold: graphs provide a formal model to analyse conversions; a complete mapping can be achieved in an incremental way by adding rule by rule; conversion rules can be graphically defined; the generation of the conversion routines corresponding to these rules can be automated; and finally, the rule-based approach allows to compile input and use-case specific conversion profiles based on a library of rules.
Link to project website: https://ifc2citygml.github.io/
NUS Research News : https://news.nus.edu.sg/research/nus-architecture-team-wins-prize-automatic-3d-modelling-cities