Curriculum Structure
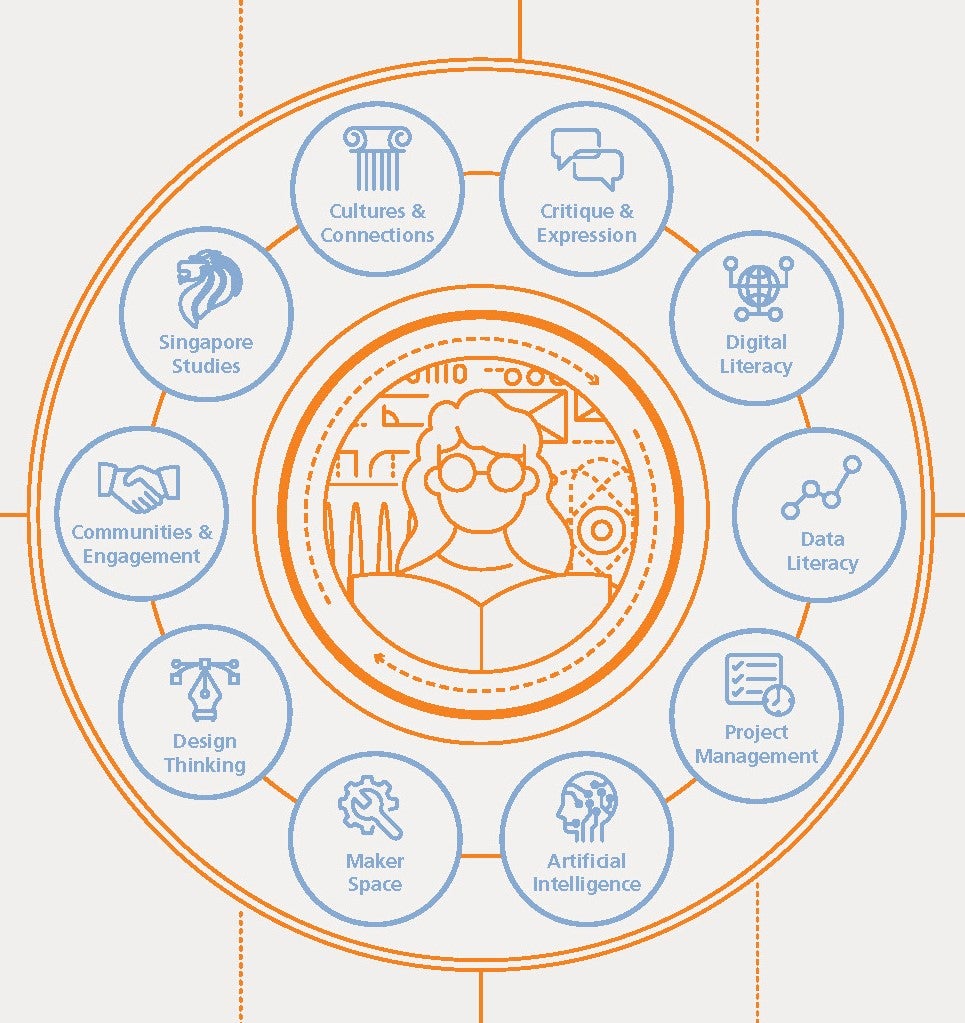 The Common Curriculum consists of 10 carefully curated pillars to give a solid foundation in interdisciplinary skills. We emphasise instilling lifelong skills via the following pillars:
|
| Curriculum Structure |
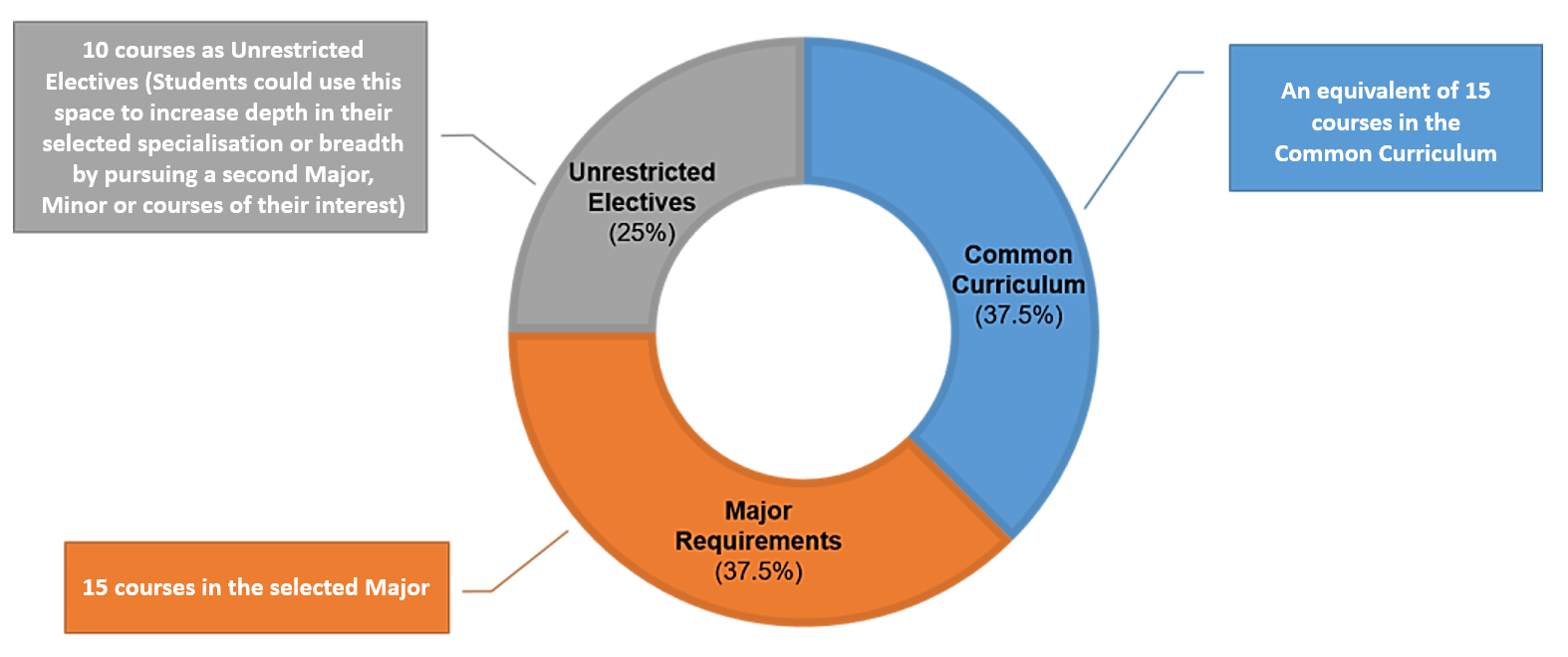
 Students should complete a total of 160 units (or the equivalent of 40 courses), comprising: Students should complete a total of 160 units (or the equivalent of 40 courses), comprising:
These aim to provide CDE students with a comprehensive and well-rounded education, preparing them for success in their chosen careers and beyond. |
| Mechanical Engineering (ME) Undergraduate Curriculum Structure (Cohort AY2025/2026 onwards) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| ME Major Requirements | Common Curriculum Requirements | Unrestricted Elective (UE) Courses | |
Engineering Core (20 Units)
Mechanical Engineering Major
|
General Education (GE) Courses (24 Units)
|
Common Courses (16 Units)
|
40 units of Unrestricted Elective Courses
(Any course open to you; may be used to fulfil requirements for specialisations, majors or minors.) |
| Subtotal = 80 Units | Subtotal = 40 Units | Subtotal = 40 Units | |
| Minimum required for graduation = 160 Units | |||
An undergraduate curriculum structure has been adopted for students enrolled in the academic year starting in August 2021. Students will read a total of 160 Units (or the equivalent of 40 courses), as shown in the following schema:
The Common Curriculum is jointly developed with industry partners who sit on the task force. It seeks to integrate knowledge and skillsets relevant to the professional training offered by both schools and to equip students with essential 21st century competencies. The Common Curriculum consists of 14 carefully curated pillars with the Integrated Project being equivalent to two courses. Choose courses from each of the 14 pillars listed below under the Common Curriculum:
![Common Curriculum Modules[1]](https://cde.nus.edu.sg/me/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2021/12/common-curriculum-modules1-1024x430.png)
Workload is measured in terms of Units, where one Unit is the equivalent of 2.5 hours of study and preparation per week. Most courses are typically 4 Units.
| Mechanical Engineering (ME) Undergraduate Curriculum Structure (Cohort AY2021/2022 onwards) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| ME Major Requirements | Common Curriculum Requirements | Unrestricted Elective (UE) Courses | |
Engineering Core (20 Units)
Mechanical Engineering Major
|
General Education (GE) Courses (24 Units)
|
Common Courses (36 Units)
|
40 units of Unrestricted Elective Courses
(Any course open to you; may be used to fulfil requirements for specialisations, majors or minors. Refer to the “Build Your Own Degree” page for more information.) |
| Subtotal = 60 Units | Subtotal = 60 Units | Subtotal = 40 Units | |
| Minimum required for graduation = 160 Units | |||
Workload is measured in terms of Units, where one Unit is the equivalent of 2.5 hours of study and preparation per week. Most courses are typically 4 Units.
More details about the requirements (within the sample semester schedules) can be found here.
Details about courses can be found here.
Degree requirements for different cohorts:
Specialisations
If you are passionate about pursuing an engineering career in one of the areas listed below, you may opt to specialise in higher years by reading technical electives from a given set of courses according to your cohort requirements. Our specialisations are in the following fields.
Additional requirements concerning specialisations can be found here.
Aeronautical Engineering
Learn advanced concepts of flight, aircraft structures, propulsion and control, and apply these in our state-of the-art laboratories with extensive testing facilities. Be inspired to work on the design and construction of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV), flapping-wing Micro Air Vehicles (MAV), and more. Our close collaboration with Temasek Labs @ NUS opens up exciting opportunities in the most advanced aerospace research facilities in Singapore.
Energy and Sustainability
You learn about traditional and alternative energy sources, as well as the science and technology of energy conversion and storage, all within the broader context of energy management, sustainability and security. Be equipped with the advanced interdisciplinary skills required to analyse, design, optimise and evaluate the technical and economic viability of energy systems. You have opportunities to put your knowledge into practice across a range of scales and systems as diverse as cooling in electronics to vehicles, buildings, desalination and power-plants, and even entire mega-cities.
Industry 4.0
The Industry 4.0 Specialisation within the Bachelor of Engineering (Computer Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, and Chemical Engineering) curriculum at NUS is a multi-disciplinary study drawing expertise from various departments. The specialisation allows students to learn about machines augmented with sensors which communicate with each other, servers, the cloud, and people to enhance autonomy, visualisation and decision making. Design systems to boost industrial productivity. The Industry 4.0 specialisation will equip students for the digitalised industry and the challenges associated.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, Industry 4.0, is revolutionising manufacturing processes by integrating operation and information technologies with the aim of increasing productivity. The advent of Industry 4.0 and availability of Big Data have transformed how industries manage operations, maintenance, and productivity. Sensor data generated from IoT-powered manufacturing systems enable the use of data analytics and machine learning for system health monitoring and optimisation.
The advent of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming production plants into cyber physical systems that generate Big Data throughout the operational life cycle. The large amounts of data and interconnectivity among machineries have led to new opportunities and challenges for the manufacturing industry. Digitalisation, a key component of Industry 4.0, achieves production optimisation through real-time monitoring of asset performance, data analytics and predictive maintenance.
Click here for more information.
Offshore Oil and Gas Technology (no longer offered to new students)
Oil and gas companies are transitioning to a lower-carbon future, supporting developments in clean energy, as well as carbon capture and carbon storage technologies. Learn about capabilities in fossil fuel extraction and how these are now being applied in innovative ways to mitigate climate change.
Robotics
A multi-disciplinary specialisation drawing expertise from various engineering fields, this specialisation allows students to take a hands-on approach to learning, through small projects in the modules and a final year project on robotics. Students will need to design and construct robotic systems or their components. As with all engineering design and implementation, students will need to communicate their design to their peers so that different components can work together or in a bigger system. With the knowledge and experience in robotics, automation, and artificial intelligence, graduates from this programme will be ready to contribute to the high-tech industries that Singapore is nurturing.
Specialisations are optional, and you would not be disadvantaged should you not specialise. Instead, you could choose technical electives from a range of ME topics to strengthen your overall ME expertise. Many of our top graduates do not specialise, yet build highly successful careers in various fields of engineering. You would receive a separate certificate of specialisation in the chosen field, in addition to the B.Eng. (ME) degree scroll.
You may apply for a specialisation at the point of application to NUS (for Aeronautical Engineering, Robotics and Industry 4.0) or later in Year 2 (for all specialisations). Your selection to and continuation in each specialisation is based on overall merit, as well as your aptitude in related foundational courses – there are no quotas on the number accepted to each specialisation.
Differentiated Pathways
(for cohorts AY2019/2020 and AY2020/2021 only)
You can have a successful career not only as a practising engineer in industry, but also as an entrepreneur or a researcher. Depending on your strengths, interests and aspirations, you improve your training in your preferred profession through one of our three differentiated education pathways. Read more about the pathways here.

